Mobile Signal Strength Recommendations
Summary
This chapter is an overview of recommended signal strength levels for different mobile service modes.
Signal Measurement
Signal strength values are defined by a few different measurements which vary even more for different service modes. These measurements are as follows:
More on these measurements in separate service mode sections.
Determining Factors of Signal Values
There are many different factors that influence signal strength and quality, including but not limited to:
- Tower load
- Proximity to the cellular tower
- Signal going through a cellular repeater
- Competing signals
- Physical barriers (mountains, buildings, trains, etc.)
- Weather
Therefore, measurements like Signal Strength (RSSI) and Signal Quality (EC/IO) do not incorporate all of the relevant factors to describe the quality of the connection. For example, you may have an excellent RSSI value of -51 dBm, but the Tower Load (the number of mobile users) in your area is very high. In this case, even though you have a great Signal Strength value, you may not achieve maximum mobile data speeds.
Disclaimers
- Both Signal Strength and Signal Quality must be considered for successful cellular data connection
- Measured or reported values vary by modem, carrier, and network environment
- There is no black/white answer to what constitutes a successful connection
- Although signal strength may appear to be adequate, throughput speeds may vary due to dependencies on cellular tower loads
2G (GSM)
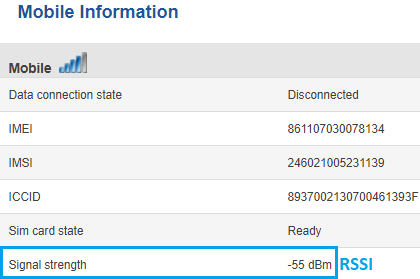
2G (GSM) Signal strength is defined by only one value: RSSI – Received Signal Strength Indicator; RSSI is a negative value, and the closer to 0, the stronger the signal.
| RSSI | Signal strength | Description |
|---|---|---|
| >= -70 dBm | Excellent | Strong signal with maximum data speeds |
| -70 dBm to -85 dBm | Good | Strong signal with good data speeds |
| -86 dBm to -100 dBm | Fair | Fair but useful, fast and reliable data speeds may be attained, but marginal data with drop-outs is possible |
| < -100 dBm | Poor | Performance will drop drastically |
| -110 dBm | No signal | Disconnection |
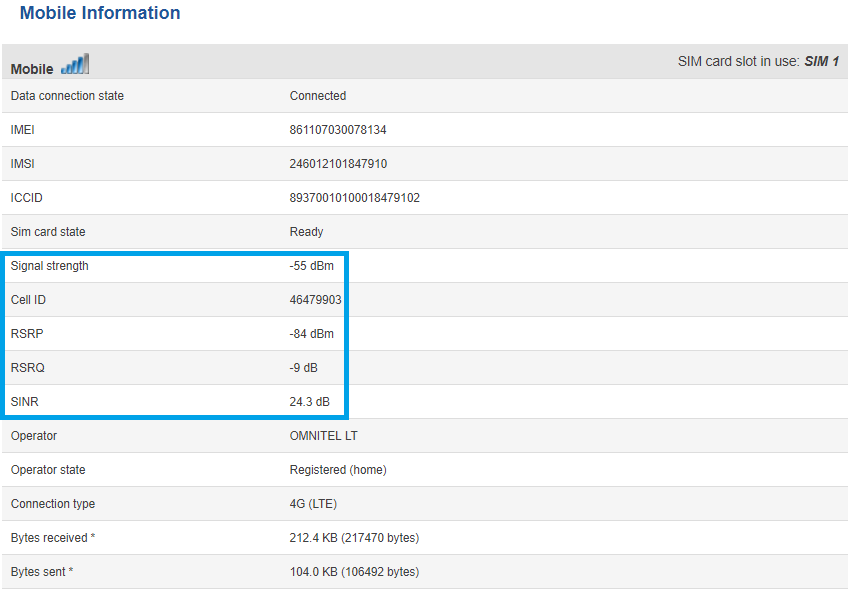
To check the 2G signal strength value of your RUT device, log in to your router's WebUI and go to the Status -> Network -> Mobile window:
3G (WCDMA, TDSCDMA, CDMA, EVDO, CDMA-EVDO)
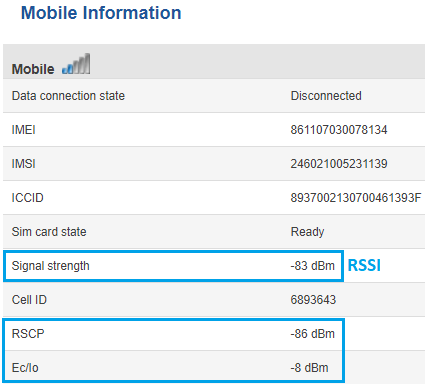
For 3G service mode, there are three relevant measurements:
- RSSI - Received Signal Strength Indicator. RSSI is a negative value, and the closer to 0, the stronger the signal
- EC/IO - indicates the downlink carrier-to-interference ratio (signal quality).EC/IO is a negative dBm value. Values closer to 0 are stronger signals
- RSCP - indicates the Received Signal Code Power
The RSSI standard values for 3G are basically the same as 2G
| RSSI | Signal strength | Description |
|---|---|---|
| >= -70 dBm | Excellent | Strong signal with maximum data speeds |
| -70 dBm to -85 dBm | Good | Strong signal with goodta speeds |
| -86 dBm to -100 dBm | Fair | Fair but useful, fast and reliable data speeds may be attained, but marginal data with drop-outs is possible |
| < -100 dBm | Poor | Performance will drop drastically |
| -110 dBm | No signal | Disconnection |
| EC/IO | Signal quality | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 to -6 | Excellent | Strong signal with maximum data speeds |
| -7 to -10 | Good | Strong signal with good data speeds |
| -11 to -20 | Fair to poor | Reliable data speeds may be attained, but marginal data with drop-outs is possible. When this value gets close to -20, performance will drop drastically |
| RSCP | Signal strength | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -60 to 0 | Excellent | Strong signal with maximum data speeds |
| -75 to -60 | Good | Strong signal with good data speeds |
| -85 to -75 | Fair | Fair but useful, fast and reliable data speeds may be attained |
| -95 to -85 | Poor | Marginal data with drop-outs is possible |
| -124 to -95 | Very poor | Performance will drop drastically, closer to -124 disconnects are likely |
To check the 3G signal strength values of your RUT device, log in to your router's WebUI and go to the Status -> Network -> Mobile window:
4G (LTE)
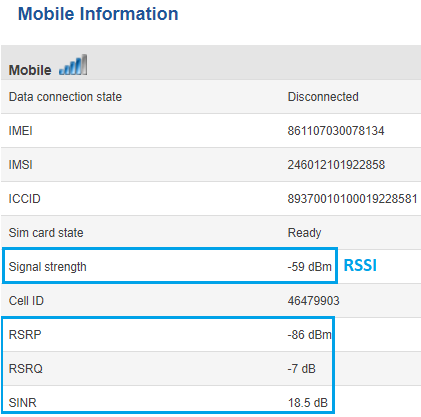
For 4G service mode, there are four relevant measurements:
- RSSI - Received Signal Strength Indicator. RSSI is a negative value, and the closer to 0, the stronger the signal
- RSRP - the Reference Signal Received Power is the power of the LTE Reference Signals spread over the full bandwidth and narrowband
- RSRQ - Reference Signal Received Quality is a C/I type of measurement and it indicates the quality of the received reference signal (similar to EC/IO)
- SINR - Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (A minimum of -20 dB SINR is needed to detect RSRP/RSRQ). Indicates the throughput capacity of the channel. As the name implies, SINR is the strength of the signal divided by
the strength of any interference
| RSRP | Signal strength | Description |
|---|---|---|
| >= -80 dBm | Excellent | Strong signal with maximum data speeds |
| -80 dBm to -90 dBm | Good | Strong signal with good data speeds |
| -90 dBm to -100 dBm | Fair to poor | Reliable data speeds may be attained, but marginal data with drop-outs is possible. When this value gets close to -100, performance will drop drastically |
| <= -100 dBm | No signal | Disnonnection |
| RSRQ | Signal quality | Description |
|---|---|---|
| >= -10 dB | Excellent | Strong signal with maximum data speeds |
| -10 dB to -15 dB | Good | Strong signal with good data speeds |
| -15 dB to -20 dB | Fair to poor | Reliable data speeds may be attained, but marginal data with drop-outs is possible. When this value gets close to -20, performance will drop drastically |
| <= -20 dB | No signal | Disconnection |
| SINR | Signal strength | Description |
|---|---|---|
| >= 20 dB | Excellent | Strong signal with maximum data speeds |
| 13 dB to 20 dB | Good | Strong signal with good data speeds |
| 0 dB to 13 dB | Fair to poor | Reliable data speeds may be attained, but marginal data with drop-outs is possible. When this value gets close to 0, performance will drop drastically |
| <= 0 dB | No signal | Disconnection |
RSSI for LTE is a calculated from several other signal related measurements: RSSI = wideband power = noise + serving cell power + interference power. For example, a 4G LTE modem might report an RSSI of -68 dBm, but:
RSRP = -102 dBm
RSRQ = -16 dB
SINR = -1.8 dB
In this case, the signal quality is actually very poor. This could be due to the device being some distance away from the LTE transmitter. It’s also possible that something is interfering with the signal, such as a building or other obstructions between the device and the tower.
| RSSI | Signal strength | Description |
|---|---|---|
| > -65 dBm | Excellent | Strong signal with maximum data speeds |
| -65 dBm to -75 dBm | Good | Strong signal with good data speeds |
| -75 dBm to -85 dBm | Fair | Fair but useful, fast and reliable data speeds may be attained, but marginal data with drop-outs is possible |
| -85 dBm to -95 dBm | Poor | Performance will drop drastically |
| <= -95 dBm | No signal | Disconnection |
To check the 4G signal strength values of your RUT device, log in to your router's WebUI and go to the Status -> Network -> Mobile window:
How do I check the signal quality on a RUT device?
WebUI
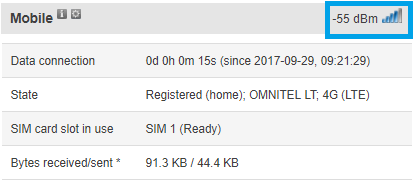
The fastest and easiest way to find out your RSSI is by checking the Overview window of your router's WebUI (web user interface). The Overview window can be reached simply by accessing your router's WebUI (the default log in information is: address: 192.168.1.1; Username: admin; Password: admin01). Once you've logged in, you will be redirected to the Overview window automatically. The Overview window contains widgets that display various information summaries about the status of your router. The RSSI value can be checked by looking at the Mobile widget that is located in the top right corner of the Overview window by default.
To get more detail about signal quality, you may want to check the Mobile Information section, which is located in Status -> Network -> Mobile. The Mobile Information window contains information about your mobile connection. Concerning signal quality, it displays Signal Strength (RSSI), RSRP, RSRQ and SINR for LTE, Signal Strength (RSSI), EC/IO and RSCP for 3G and Signal Strength (RSSI) for 2G.
Router LEDs
You can also find out the router's signal strength by checking the Signal Strength LEDs on the front panel of your router. This will not provide you with a numeric value of signal strength. The LEDs indicate RSSI value in bar form (similar to a cell phone)
A picture of the front panel of a RUT950 router. Signal Strength LEDs are highlighted
Advanced
To get the most detailed information about your signal quality values you can use gsmctl commands when logged in via CLI or SSH.
gsmctl commands are designed to get information from your router's modem. The user sends a gsmctl command to the router; the router then converts that command to an AT and sends it to the modem; the modem responds with the requested information, which the router then translates to the information that you have requested.
gsmctl commands concerning signal quality:
- gsmctl -q - returns the current RSSI value (available with all services modes)
- gsmctl -W - returns the current RSRP value (only with 4G)
- gsmctl -M - returns the current RSRQ value (only with 4G)
- gsmctl -Z - returns the current SINR value (only with 4G)
- gsmctl -E - returns the current EC/IO value (only with 3G)
- gsmctl -X - returns the current RSCP value (only with 3G)
- gsmctl -h - provides you with a list of all possible gsmctl commands
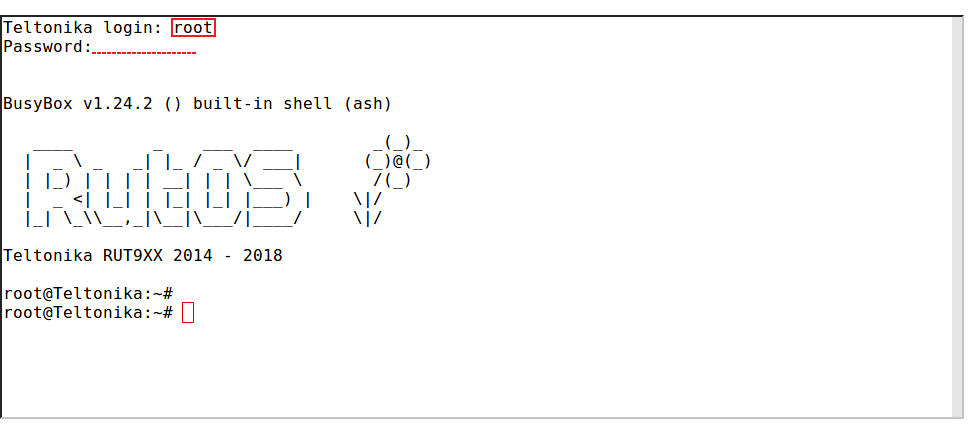
CLI
CLI (Command Line Interface) allows you to enter and execute commands into the router's terminal. CLI can be found in the Services section (Services -> CLI). The default Username for logging into CLI is root and the password is your router's password (default: admin01). Once you've logged in you should be greeted by a window like this:
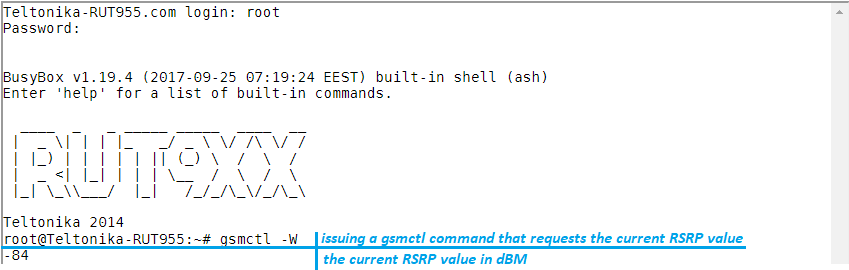
An example of a gsmctl command usage with CLI. In the example, the user is requesting the current RSRP value by issuing the gsmctl -W command
SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. If you are using a Linux type Operating System, login to a RUT router via SSH through the Terminal app. If you are using Windows, you will need to download an app to login via SSH, for example, PuTTY.
The login sequence is very similar to CLI, except you will also need to specify the router's LAN address. The login string on a Linux based OS should like this: ssh username@routers_lan. After this you will be prompted to enter the router's password (default: admin01). The login string to a default RUT device would look like this: ssh [email protected] with the password being admin01.
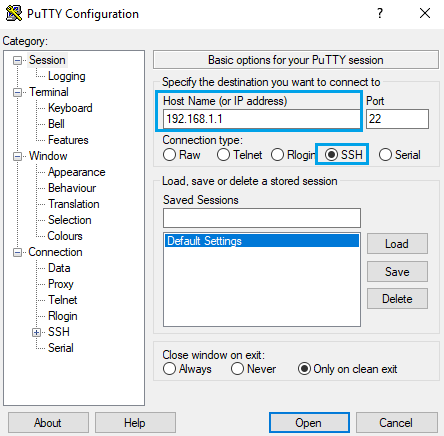
To login via SSH using PuTTY on a Windows OS, open the PuTTY app, where you will be required to enter your router's LAN IP address in the Host name (or IP address) field. Below is an example of how it looks
Once you've entered your router's LAN IP address, click the Open button after which you will be greeted with a similar window to CLI, where you will prompted to enter a user name (default: root) and password (default: admin01). After this you can start using gsmctl commands in an identical manner to CLI.
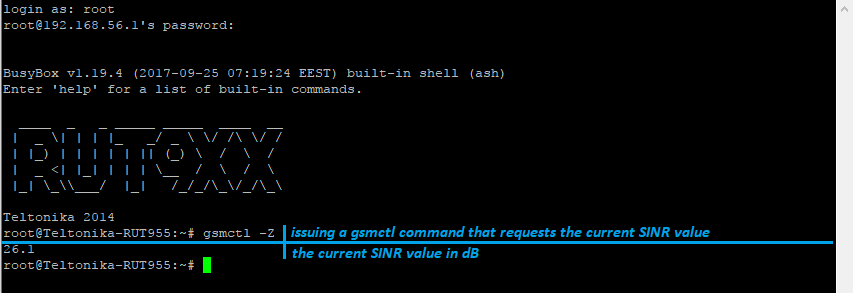
An example of a gsmctl command usage with SSH. In the example, the user is requesting the current SINR value by issuing the gsmctl -Z command