Difference between revisions of "Monitoring via MQTT"
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | After the client sends a message containing of these parameters, the Publisher will send a response message containing the value of the requested parameter to the topic '''router/<SERIAL>/parameter_name''', where '''parameter_name''' is the name of the requested parameter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Configuration examples mqtt scheme v1.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | It should also be noted that, according to the MQTT protocol, topic names are case-sensitive, for example topic '''router''' is not the same as topic '''RoUtEr'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Configuring | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 30 November 2017
Main Page > General Information > Configuration Examples > Router control and monitoring > Monitoring via MQTTSummary
MQTT (MQ Telemetry Transport or Message Queue Telemetry Transport) is an ISO standard (ISO/IEC PRF 20922) publish-subscribe-based messaging protocol. It works on top of the TCP/IP protocol. It is designed for connections with remote locations where a "small code footprint" is required or the network bandwidth is limited. The publish-subscribe messaging pattern requires a message broker. This chapter is a guide on how to configure a basic MQTT setup on RUT routers.
How MQTT works
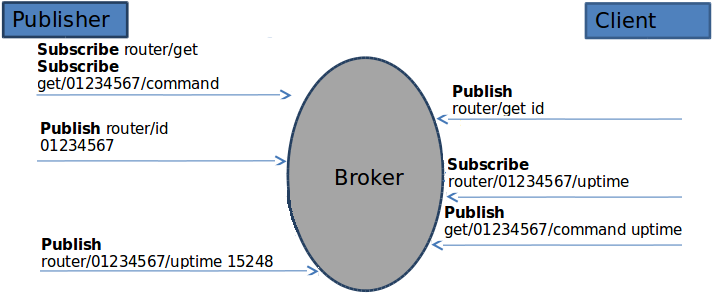
First lets look over how MQTT works on RUT routers. An MQTT connection takes place between two Clients and a Broker. A RUT router can be Broker, a Client or both. The MQTT Publisher (Client) present in RUT routers subscribes to two topics by default: router/get and get/<SERIAL>/command, where <SERIAL> is the router's serial number. When a third party client connects to the Broker, it sends the message id to the the topic router/get. The publisher then sends a response containing its serial number to the topic router/id. Now that the Client knows the router's serial number it can ask for values of various parameters by sending requests to the topic router/<SERIAL>/parameter_name. The MQTT Publisher can send responses containing values of these system parameters:
| Parameter name | Parameter description |
|---|---|
| temperature | Temperature of the module in 0.1 degrees Celsius |
| operator | Current operator’s name |
| signal | Signal strength in dBm |
| network | Current network type (2G, 3G, 4G) |
| connection | Data connection status |
| wan | WAN IP address |
| uptime | System uptime in seconds |
| name | Router’s name |
| digital1 | Value of digital input no. 1 |
| digital2 | Value of digital input no. 2 |
| analog | Value of analog |
After the client sends a message containing of these parameters, the Publisher will send a response message containing the value of the requested parameter to the topic router/<SERIAL>/parameter_name, where parameter_name is the name of the requested parameter.
It should also be noted that, according to the MQTT protocol, topic names are case-sensitive, for example topic router is not the same as topic RoUtEr.
==Configuring