Template:RelayD configuration with IPv4+IPv6 functionality
The information in this page is updated in accordance with 00.07.08 firmware version.
Introduction
This article contains instructions on how to do UCI-based configuration for setting up RelayD with IPv4+IPv6 support on Teltonika Networks routers.
Tunnelbroker configuration
Tunnelbroker is a website operated by Hurricane Electric, a leading provider of internet services and networking solutions. The website provides a service called Hurricane Electric IPv6 Tunnel Broker, which allows users to create an IPv6 tunnel between their network and Hurricane Electric's network. This allows users to connect their devices to the internet using the IPv6 protocol, even if their internet service provider (ISP) does not support IPv6.
Login
Go to tunnelbroker.net and log into your account. If you don't have a registered account then you will need to create one - click register.

IPv6 to IPv4 tunnel creation
Setup IPv6 over IPv4, also known as 6in4 IPv6 transition mechanism. To create a new tunnel:
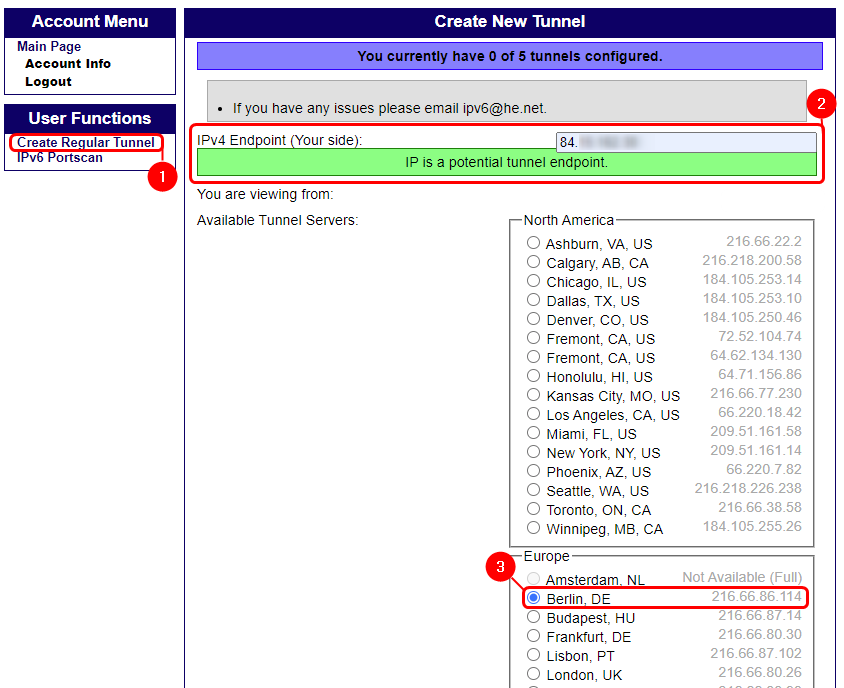
- Click on create regular tunnel,
- Enter your public IP (it will light up green, if the tunnel can be created with this IP),
- Select the desired tunnel server,
To establish the tunnel, at the bottom of the page, you should see Create tunnel.
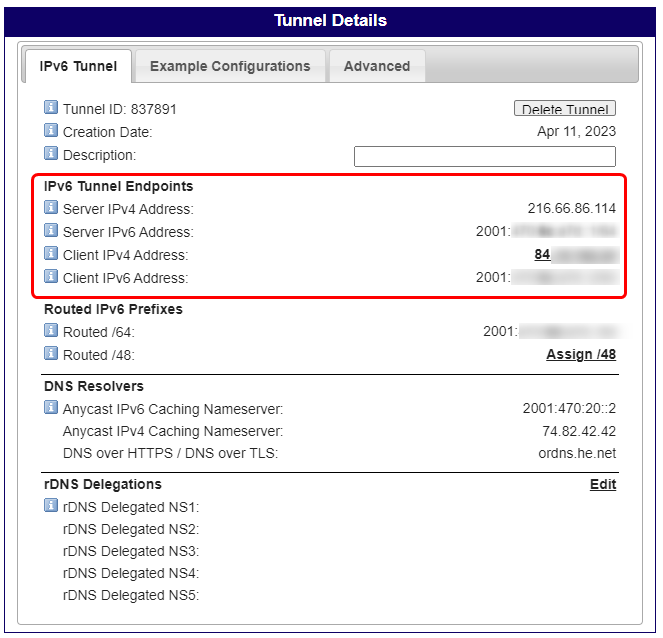
After successful tunnel creation, you will be prompt to tunnel details window.
To create a a tunnel instance on your RUT router, navigate to example configurations, there, select OpenWRT Barrier Breaker. and paste the following commands into your router CLI.
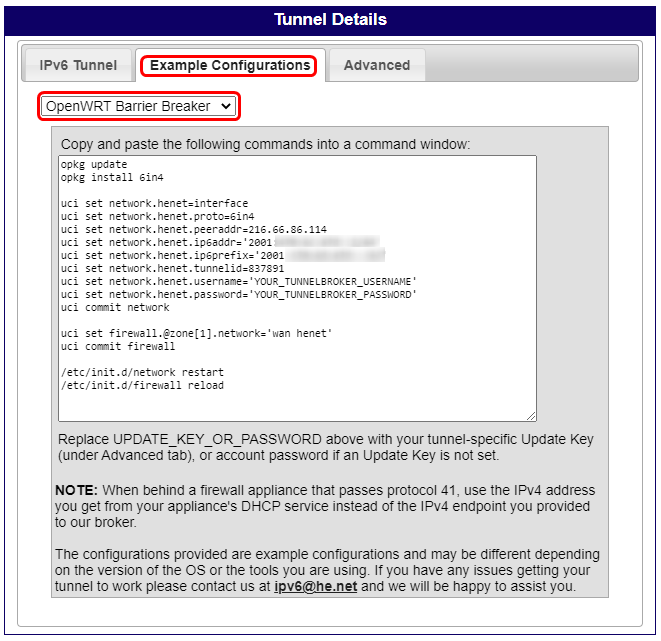
Note: Do not forget to replace YOUR_TUNNELBORKER_USERNAME and YOUR_TUNNELBROKER_PASSWORD with your TunnelBroker account username and password.
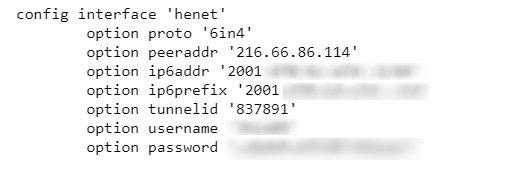
Use the cat /etc/config/network command in routers CLI to see if the new interface was successfully created.
Router configuration
Relayd and interface configuration using UCI
Relay is a daemon (computer program that runs as a background process) used to relay and dynamically redirect incoming connections to a target host. Its main purpose in RUTxxx routers is to extend the wireless network. For example, when RUTxxx is in STA Wireless Station mode, it can be used to bridge WAN and LAN interfaces to create a larger Wireless network.
Unified Configuration Interface (UCI) is a small utility written in C (a shell script-wrapper is available as well) and is intended to centralize the whole configuration of a device running on OpenWrt.
Relayd installation
Install relayd package if needed, skip this step on RUTX series devices or if you already installed it on your router
opkg update --force_feeds /etc/opkg/openwrt/distfeeds.conf opkg install relayd
WiFi client configuration
Add WiFi interface to make your router act as a WiFi client (connect to another AP)
uci add wireless wifi-iface uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1]=wifi-iface
Add new WiFi interface to 2.4ghz device, can specify 'radio1' for 5ghz
uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].device='radio0' uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].mode='sta' uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].network='wifi_wan'
Change SSID here to an SSID that the router will be connecting to
uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].ssid='RUT1_SSID'
Change BSSID here to BSSID that the router will be connecting to (L2 address)
uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].bssid='RUT1_BSSID'
Use appropriate encryption method, PSK2 = WPA2-PSK here
uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].encryption='psk2'
Change secret to appropriate one
uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].key='SSID_PASSWORD' uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].disabled='0' uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].skip_inactivity_poll='0' uci set wireless.@wifi-iface[-1].wifi_id='wifi1'
IPv4 interface creation
Create a new interface IPv4 for WiFi WAN.
uci set network.wifi_wan=interface uci set network.wifi_wan.proto='dhcp' uci set network.wifi_wan.metric='6' uci set network.wifi_wan.disabled='0' uci set network.wifi_wan.force_link='0' uci set network.wifi_wan.broadcast='0'
Set mwan3 settings for new interface
uci set mwan3.wifi_wan=interface uci set mwan3.wifi_wan.enabled='0' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan.interval='3' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan.family='ipv4' uci add mwan3 condition uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].interface='wifi_wan' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].track_method='ping' uci add_list mwan3.@condition[-1].track_ip='1.1.1.1' uci add_list mwan3.@condition[-1].track_ip='8.8.8.8' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].reliability='1' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].count='1' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].timeout='2' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].down='3' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].up='3' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan_member_mwan=member uci set mwan3.wifi_wan_member_mwan.interface='wifi_wan' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan_member_mwan.metric='1' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan_member_balance=member uci set mwan3.wifi_wan_member_balance.interface='wifi_wan' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan_member_balance.weight='1' uci add_list mwan3.mwan_default.use_member='wifi_wan_member_mwan' uci add_list mwan3.balance_default.use_member='wifi_wan_member_balance'
IPv6 interface creation
Create a new IPv6 interface for WiFi WAN
uci set network.wifi_wan6=interface uci set network.wifi_wan6.proto='dhcpv6' uci set network.wifi_wan6.metric='6' uci set network.wifi_wan6.disabled='0' uci set network.wifi_wan6.force_link='0' uci set network.wifi_wan6.reqaddress='try' uci set network.wifi_wan6.reqprefix='auto' uci set network.wifi_wan6.device='@wifi_wan'
Set proper ipv6 settings for wifi_wan6 iface
uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6=interface uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6.enabled='0' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6.interval='3' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6.family='ipv6' uci add mwan3 condition uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].interface='wifi_wan6' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].track_method='ping' uci add_list mwan3.@condition[-1].track_ip='2606:4700:4700::1111' uci add_list mwan3.@condition[-1].track_ip='2001:4860:4860::8888' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].reliability='1' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].count='1' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].timeout='2' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].down='3' uci set mwan3.@condition[-1].up='3' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6_member_mwan=member uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6_member_mwan.interface='wifi_wan6' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6_member_mwan.metric='1' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6_member_balance=member uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6_member_balance.interface='wifi_wan6' uci set mwan3.wifi_wan6_member_balance.weight='1' uci add_list mwan3.mwan_default.use_member='wifi_wan6_member_mwan' uci add_list mwan3.balance_default.use_member='wifi_wan6_member_balance' uci set mwan3.default_rule_ipv6=rule uci set mwan3.default_rule_ipv6.dest_ip='::/0' uci set mwan3.default_rule_ipv6.use_policy='mwan_default' uci set mwan3.default_rule_ipv6.family='ipv6'
LAN interface configuration
Configure a LAN interface accordingly.
uci set network.lan_repeater=interface uci set network.lan_repeater.proto='relay' uci set network.lan_repeater.lan_mark='lan' uci set network.lan_repeater.enabled='1' uci set network.lan_repeater.network='lan wifi_wan'
Set DHCP settings for LAN interface (disable dhcp on LAN) and enable IPv6 relay on wifi_wan interface and
uci set dhcp.lan.ignore='1' uci set dhcp.lan.ra='relay' uci set dhcp.lan.dhcpv6='relay' uci set dhcp.lan.ndp='relay'
uci set dhcp.wifi_wan=dhcp uci set dhcp.wifi_wan.ra='relay' uci set dhcp.wifi_wan.dhcpv6='relay' uci set dhcp.wifi_wan.master='1' uci set dhcp.wifi_wan.ndp='relay'
Firewall configuration
Set firewall zone, using WAN firewall zone for newly created WiFi WAN network interface.
uci set firewall.@zone[1].network='wan wan6 mob1s1a1 mob1s2a1 wifi_wan'
Commit changes
Save all the changes and restart the configuration
uci commit reload_config
Testing the setup
If you've taken all of the steps described above, the configuration is done. But as with any other configuration, it is always wise to test the set up in order to make sure that it works properly.
- Check what IP address are you getting on What is my IP address website.
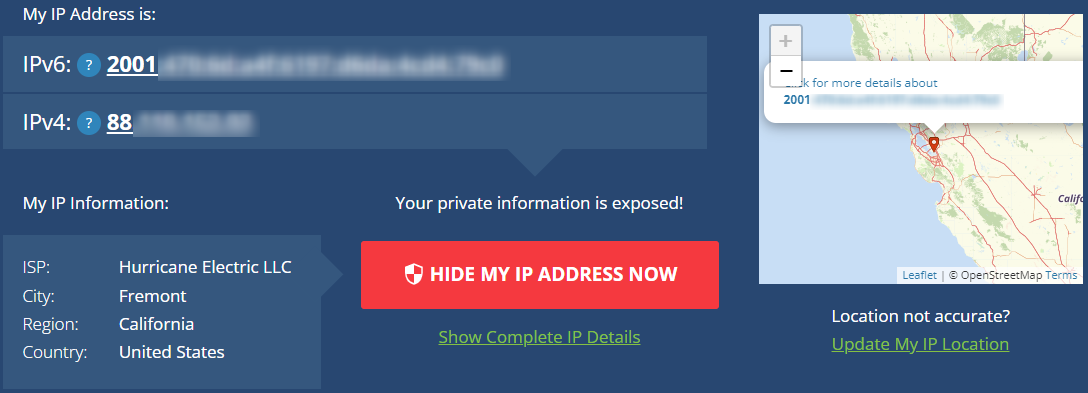
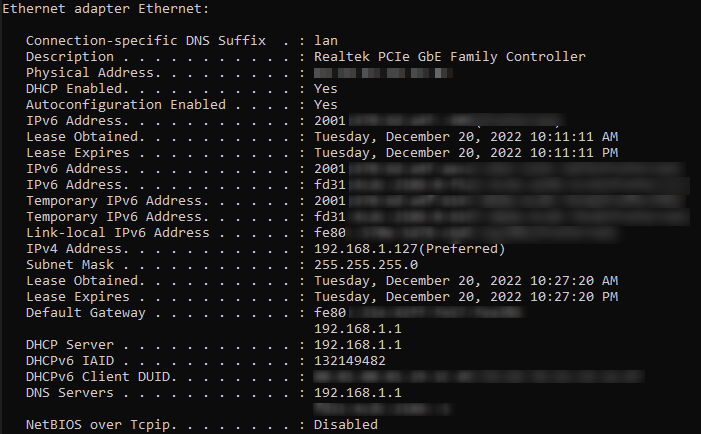
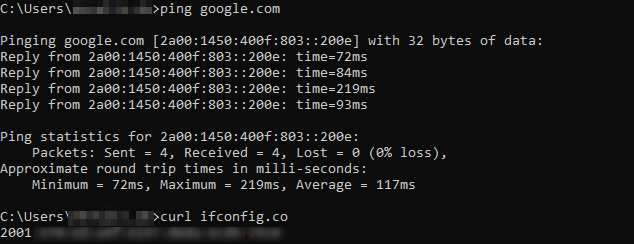
- You can also check what IP address you are getting via command line interface.
See also
More information about RelayD
External links
More about TunnelBroker.net
